Characteristics of Living things
- They are all made up of : Cells, either only one (unicellular organism) or more (pluricellular)
- They do the vital functions: (nutrition, interaction and reproduction)
- They all have a similar composition
Biomolecules:
Inorganic biomolecules:water and mineral salts
Organic molecules: Carbohydrates, Fats or lipids ,Proteins and Nucleic acids.
NUTRITION
Autotrophs (they CAN produce their own organic compounds),
either they get Energy from the SUN: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
or from Chemical _Ractions: CHEMOSYNTHESIS
Heterotrophs (they cannot produce their own organic compounds)
INTERACTION
Response to a change in the environment.
STIMULUS --RESPONSE
REPRODUCTION
Sexual: 2 individuals needes (male + female) , 2 sexual cells (GAMETES), diverse offspring generated
Asexual: only ONE individual implied / genetically identical offspring
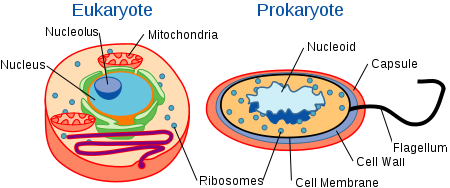
- All living things are composed by cells
- Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things
- New cells are produced by existing cells
Kingdom | When Evolved | Structure | Photosynthesis |
Prokaryotic: |
|
|
|
Bacteria | 3 to 4 billion years ago | Unicellular | Sometimes |
Archaea | 3 to 4 billion years ago | Unicellular | No |
Eukaryotic: |
|
|
|
Protozoa | 1.5 billion years ago | Unicelular | No |
Chromista | 1.2 billion years ago | Unicellular | Originally, but sometimes lost; Chlorophyll c |
Fungi | 1 billion years ago | Unicellular or Multicellular | No |
Animalia | 700 million years ago | Multicellular | No |
Plantae | 500 million years ago | Multicellular | Yes; Chlorophyll a, b, and c |


No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario